IPA
There are 19 vowels in the English language but only six letters are used to represent them. This means there is a many-to-one correspondence between vowels and letters, that is different vowels correspond to the same letter. This is unfortunate because the native english speakers are not forced to develop conscious access to their vowels.
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) was designed to provide a one-to-one correspondence between letters and sounds (phonemes) of any language. Learning the IPA is low hanging fruit, in the quest to develop specialized language abilities and raise verbal IQ.
The IPA was developed with the now obsolete Bell( tongue-height) vowel model. The vowels are arranged in a grid to cover the formant plot of vowel frequencies. The reason why the axes of the formant plot are inverted is because the first formant was thought to be negatively proportional to tongue height and the second formant negatively proportional to the forwardness or backness of the tongue.
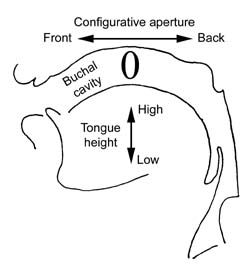
However, I believe this correspondence between symbols and formant frequencies is a malinvestment. We perceive the articulation of a vowel, as described by the Wood vowel model, rather than the formant frequencies. Thus we will give each articulation of the Wood vowel model a symbol from the IPA. This is sensible because, although formants vary significantly across accents, the articulations are relatively unchanged.
| Tense | Lax | Constriction | Jaw | Lips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i (Fleece) | ɪ (Kit) | Upper Hard palate | Closed | Spread |
| e (Air) | ɛ (Dress) | Hard Palate | Open | Spread |
| u (Goose) | ʊ (Foot) | Soft Palate | Closed | Rounded |
| ɔ (Thought) | ɒ (Lot) | Upper Pharynx | Open | Rounded |
| ɑ (Bath) | ʌ (Strut) | Lower Pharynx | Open | Spread |
| æ (Trap) | Lower Pharynx | Open | Spread | |
| ɜ (Earth) | ə (The) | Unconstricted | Closed | Spread |
Diphthongs are vowels that start at one vowel and end at another.
| IPA | English |
|---|---|
| eɪ | Tay |
| aɪ | Tie |
| aʊ | Tau |
| oʊ | Toe |
| ɔɪ | Toy |
The a symbol represents a vowel close to ʌ and o represents a vowel close to ɔ.
The consonants are much easier to learn since there nearly is a one-to-one correspondence between groups of letters and consonant sounds in english.
Consonants are categorized by the place in the vocal tract the tongue makes contact with when producing them.
In a stop consonant, the tongue blocks the vocal tract completely at a point. As this block is released, there is a burst of air as the build up of air pressure breaks the seal made by the tongue. Each place of articulation yields two stop consonants depending on whether the vocal cords are engaged or not during release. If the vocal cords are engaged the consonant is said to be voiced and unvoiced otherwise.
| Unvoiced | Voiced | Place of Articulation |
|---|---|---|
| p | b | Labial |
| t | d | Dental |
| k | g | Velar |
In a nasal, the air flow is blocked in the mouth as in a stop consonant, but this time the soft palate is lowered allowing the air to flow though the nose, resulting in a hum.
| Voiced | Place of Articulation |
|---|---|
| m | Labial |
| n | Dental |
| ŋ (ng) | Velar |
In a fricative, the tongue creates a narrow constriction at a point such that the air flow is pushed though a bottle neck, creating turbulence, resulting in a hissing sound.
| Unvoiced | Voiced | Place of Articulation |
|---|---|---|
| f | v | Labial-dental |
| θ (thigh) | ð (thy) | Dental |
| s | z | Alveolar |
| ʃ (shone) | ʒ (Jean-french) | Post-Alveolar |
An affricate is a stop consonant released into a fricative.
| Unvoiced | Voiced |
|---|---|
| tʃ (cheap) | dʒ (jeep) |
An approximant is where the vocal tract is constricted as in a fricative but not enough to create turbulence, but not so open to produce the formant widths that could be recognized as a vowel.
| Voiced | Place of Articulation | Approximating Vowel |
|---|---|---|
| w | Pharyngeal | ɔ (Thought) |
| ɹ (ray) | Alveolar | |
| j (yay) | Palatal | i (Fleece) |
In a lateral approximant, the center of the vocal tract is obstructed but air flows free around the sides of the tongue.
| Voiced | Place of Articulation |
|---|---|
| l (lay) | Alveolar |
| Unvoiced | Place of Articulation |
|---|---|
| h (hay) | Glottal |
| IPA | English |
|---|---|
| p | p |
| t | d |
| k | k |
| b | b |
| d | d |
| g | g |
| m | m |
| n | n |
| ŋ | ng |
| f | f |
| v | v |
| θ | thy |
| ð | thigh |
| s | s |
| z | z |
| ʃ | sh(shone) |
| ʒ | Jean(french) |
| l | l |
| w | w |
| r | r |
| j | yes |
| h | h |
| tʃ | cheap |
| dʒ | jeep |
 Speech School
Speech School